Intent
- Defer object creations to subclasses that know what kinds of objects they need to create
Structure
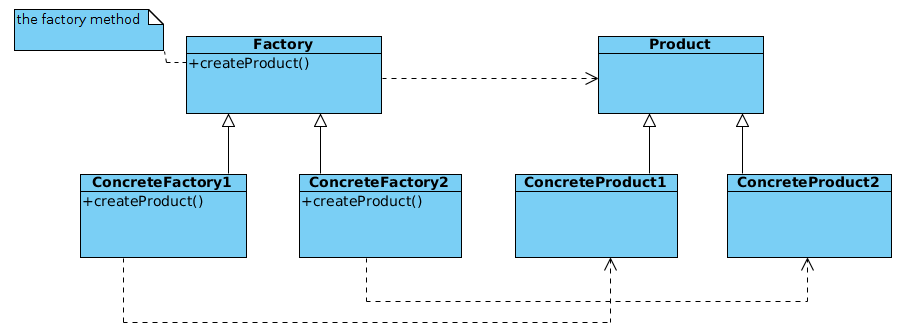
In the diagram, Factory defines a method to create a Product. This method can be an actual implementation, in which case it acts as the default implementation. If any subclass needs to create another Product rather than the default, it can override the default implementation to create its desired Product. Alternatively, the method can be an abstract method to enforce the subclasses to define the method themselves.
Applicable contexts
- There exist two class hierarchies and the objects of one of them, e.g.,
Factory, need to use those of the other, e.g.,Product. - A class does not know exactly which objects to instantiate, but its subclasses do.
- You want to defer the object instantiation to the subclasses for some other reasons.
Benefits
- Provide a way to change how objects are created at runtime
Example
References
[1] Factory method, The GOF book